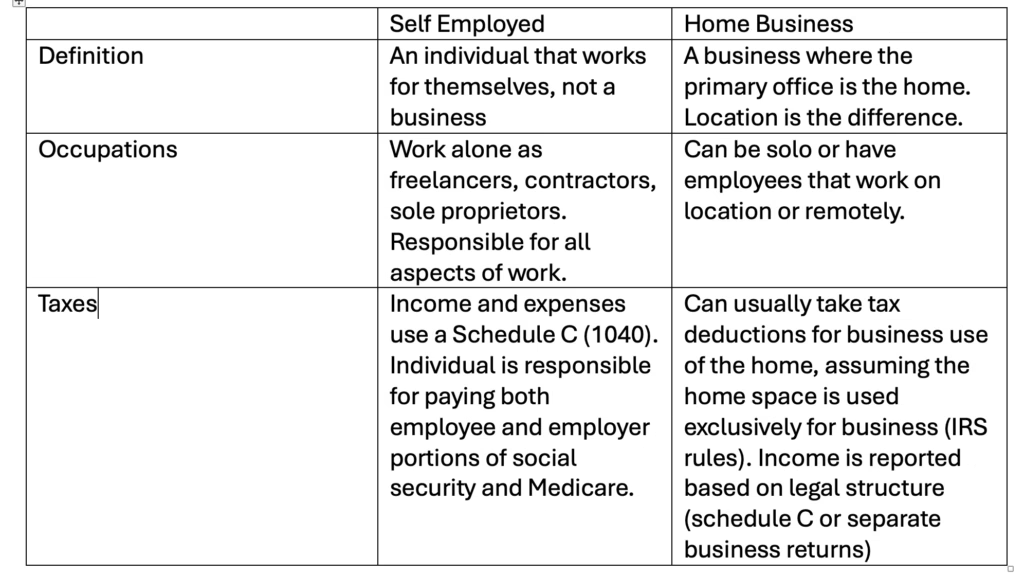
An overview of self-employment vs a home business. While similar in some ways, there are some differences.
How to Start and Plan a Home Business
- Foundational & Planning Resources:
- Business Idea and Market Research:
- Market Analysis: Understanding your target audience, market demand, size, and competition is crucial.2
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Consider testing and refining your idea with a scaled-down version to save time and resources.
- Business Plan: A detailed plan should include:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Market Analysis
- Product or Service Description3
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Financial Projections4
- Funding Requirements
- Dedicated Workspace: Even if it's a corner of a room, a designated and organized area helps with productivity and professionalism.5
- Tools and Technology:
- Reliable computer, high-speed internet (consider eSIM for flexibility), printer, phone.
- Industry-specific software or tools (e.g., design software, editing tools).
- Legal & Financial Resources:
- Business Structure: Research and choose the appropriate legal structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, corporation).6
- Licenses and Permits: Depending on your industry and location, you'll need to research and obtain necessary home occupation permits, business licenses, and professional licenses.7
- Business Bank Account: Keep personal and business finances separate for easier bookkeeping and financial tracking.8
- Accounting Software: Tools like QuickBooks or FreshBooks help track income, expenses, and taxes.9
- Insurance: Obtain general liability insurance and other policies relevant to your business to protect assets and liabilities.10
- Tax Obligations: Understand your tax responsibilities and consider consulting a financial advisor or accountant.
- Funding:
- Self-funding (bootstrapping): Using personal savings or funds from family/friends.11
- Small Business Loans: Explore traditional bank loans or SBA-guaranteed loans (e.g., through SBA's Lender Match).12
- Venture Capital: For high-growth companies, venture capital firms or angel investors might provide funding in exchange for equity.13
- Crowdfunding: A popular option for creative works or physical products.
- Grants: Look into government grants (e.g., Grants.gov, Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program) and private grants (e.g., FedEx Small Business Grant Contest, Amazon Small Business Grant, Amber Grant for women entrepreneurs).
- Legal Advice:
- LegalZoom: Offers online tools and attorney guidance for business formation, trademark registration, contracts, and more.14
- LegalShield: Provides access to legal consultation, document review, and other services for a monthly fee.
- NFIB Small Business Legal Center: Educates small business owners on relevant laws and advocates for small businesses in court (cannot offer individual legal advice).15
III. Operational & Productivity Resources:
- Project Management Tools: Trello or Asana can help organize tasks, set deadlines, and monitor progress.16
- Communication Tools: Slack or Zoom for internal team communication and virtual meetings.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Tools like Salesforce, HubSpot CRM, or Zoho CRM help manage customer interactions and streamline sales processes.17
- Cloud Storage Solutions: Google Drive or Dropbox for secure document storage and sharing.18
- E-signature/E-notary Services: For legal document signing and notarization, if available in your state.
- Marketing & Sales Resources:
- Online Presence: Develop a professional website to showcase offerings and pricing.
- Branding: Create a strong brand identity.
- Target Audience Understanding: Crucial for effective marketing.
- Email Marketing Platforms: Mailchimp, Constant Contact, or Klaviyo for automated campaigns and personalized messages.
- Social Media Management Tools: Buffer or Hootsuite for scheduling and managing social media posts.19
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) & Website Tools:
- Google Analytics (track website visitors)20
- SEMrush, Ahrefs (keyword research, competitor analysis, content optimization)
- Google Search Console (monitor website performance in search results)21
- BrightLocal (for local businesses to manage citations, reviews, and rankings)
- Google My Business Profile (essential for local SEO)22
- Advertising Platforms: Meta for Business (Facebook & Instagram Ads), Google Ads.
- Referral Programs: Incentivize customers to refer new business.23
- Content Marketing: Create valuable blog posts, videos, or other content to attract and engage your audience.
- Reputation Management: Encourage customer reviews (e.g., Google reviews).
- Networking and Educational Platforms:
- LinkedIn: Connect with industry leaders, potential clients, and other entrepreneurs.24
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera or Udemy for business strategies and skill development.
- HubSpot Academy, Neil Patel's Blog, Moz: Offer free educational resources on digital marketing.25
- Government & Support Resources:
- U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA): A primary resource for small businesses, offering:
- Free business counseling and training through partners like Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs), SCORE Business Mentors, Veterans Business Outreach Centers (VBOCs), and Women's Business Centers (WBCs).
- SBA-guaranteed business loans.
- Disaster assistance.
- Federal contracting assistance.
- U.S. Department of the Treasury: Provides assistance programs, including tax credits for small businesses.26
- General Services Administration (GSA): Offers small business resources, including information on federal contract opportunities.27
- Local Chambers of Commerce: Often provide local networking opportunities and resources.
By leveraging these resources, home business owners can set themselves up for success, navigate challenges, and foster growth.

How to Start and Plan a Home Business
- Foundational & Planning Resources:
- Business Idea and Market Research:
- Market Analysis: Understanding your target audience, market demand, size, and competition is crucial.2
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP): Consider testing and refining your idea with a scaled-down version to save time and resources.
- Business Plan: A detailed plan should include:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Market Analysis
- Product or Service Description3
- Marketing and Sales Strategy
- Financial Projections4
- Funding Requirements
- Dedicated Workspace: Even if it's a corner of a room, a designated and organized area helps with productivity and professionalism.5
- Tools and Technology:
- Reliable computer, high-speed internet (consider eSIM for flexibility), printer, phone.
- Industry-specific software or tools (e.g., design software, editing tools).
- Legal & Financial Resources:
- Business Structure: Research and choose the appropriate legal structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, LLC, partnership, corporation).6
- Licenses and Permits: Depending on your industry and location, you'll need to research and obtain necessary home occupation permits, business licenses, and professional licenses.7
- Business Bank Account: Keep personal and business finances separate for easier bookkeeping and financial tracking.8
- Accounting Software: Tools like QuickBooks or FreshBooks help track income, expenses, and taxes.9
- Insurance: Obtain general liability insurance and other policies relevant to your business to protect assets and liabilities.10
- Tax Obligations: Understand your tax responsibilities and consider consulting a financial advisor or accountant.
- Funding:
- Self-funding (bootstrapping): Using personal savings or funds from family/friends.11
- Small Business Loans: Explore traditional bank loans or SBA-guaranteed loans (e.g., through SBA's Lender Match).12
- Venture Capital: For high-growth companies, venture capital firms or angel investors might provide funding in exchange for equity.13
- Crowdfunding: A popular option for creative works or physical products.
- Grants: Look into government grants (e.g., Grants.gov, Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program) and private grants (e.g., FedEx Small Business Grant Contest, Amazon Small Business Grant, Amber Grant for women entrepreneurs).
- Legal Advice:
- LegalZoom: Offers online tools and attorney guidance for business formation, trademark registration, contracts, and more.14
- LegalShield: Provides access to legal consultation, document review, and other services for a monthly fee.
- NFIB Small Business Legal Center: Educates small business owners on relevant laws and advocates for small businesses in court (cannot offer individual legal advice).15
III. Operational & Productivity Resources:
- Project Management Tools: Trello or Asana can help organize tasks, set deadlines, and monitor progress.16
- Communication Tools: Slack or Zoom for internal team communication and virtual meetings.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Tools like Salesforce, HubSpot CRM, or Zoho CRM help manage customer interactions and streamline sales processes.17
- Cloud Storage Solutions: Google Drive or Dropbox for secure document storage and sharing.18
- E-signature/E-notary Services: For legal document signing and notarization, if available in your state.
- Marketing & Sales Resources:
- Online Presence: Develop a professional website to showcase offerings and pricing.
- Branding: Create a strong brand identity.
- Target Audience Understanding: Crucial for effective marketing.
- Email Marketing Platforms: Mailchimp, Constant Contact, or Klaviyo for automated campaigns and personalized messages.
- Social Media Management Tools: Buffer or Hootsuite for scheduling and managing social media posts.19
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO) & Website Tools:
- Google Analytics (track website visitors)20
- SEMrush, Ahrefs (keyword research, competitor analysis, content optimization)
- Google Search Console (monitor website performance in search results)21
- BrightLocal (for local businesses to manage citations, reviews, and rankings)
- Google My Business Profile (essential for local SEO)22
- Advertising Platforms: Meta for Business (Facebook & Instagram Ads), Google Ads.
- Referral Programs: Incentivize customers to refer new business.23
- Content Marketing: Create valuable blog posts, videos, or other content to attract and engage your audience.
- Reputation Management: Encourage customer reviews (e.g., Google reviews).
- Networking and Educational Platforms:
- LinkedIn: Connect with industry leaders, potential clients, and other entrepreneurs.24
- Online Courses: Platforms like Coursera or Udemy for business strategies and skill development.
- HubSpot Academy, Neil Patel's Blog, Moz: Offer free educational resources on digital marketing.25
- Government & Support Resources:
- U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA): A primary resource for small businesses, offering:
- Free business counseling and training through partners like Small Business Development Centers (SBDCs), SCORE Business Mentors, Veterans Business Outreach Centers (VBOCs), and Women's Business Centers (WBCs).
- SBA-guaranteed business loans.
- Disaster assistance.
- Federal contracting assistance.
- U.S. Department of the Treasury: Provides assistance programs, including tax credits for small businesses.26
- General Services Administration (GSA): Offers small business resources, including information on federal contract opportunities.27
- Local Chambers of Commerce: Often provide local networking opportunities and resources.
By leveraging these resources, home business owners can set themselves up for success, navigate challenges, and foster growth.